WiFi is all around us, in our homes, offices, schools, restaurants and coffee shops. WiFi connects us to the internet using 2.5 Ghz or 5 Ghz radio frequency signals. We don’t see it, so we typically do not think about it. In most cases, low levels of WiFi radio frequency (RF) are completely harmless. However, improper placement of equipment can cause potential health issues; with real physiological effects.
Is Wifi Harmful
That question is coming up more and more these days and the answers vary wildly. Tech Wellness has a good article titled: Is My Wifi Safe? Distance is Key… plenty of great information from various sources. Their recommendation is ten feet from any Wifi source.
WiFi Safety Studies
Most people are unaware of WiFi studies. Both the US Government National Institute of Health and Science Direct report negative heath effects on prolonged exposure. Below are a collection of wifi rat studies using 2G, 3G , 2.4Ghz and 5 Ghz RF. This is recommended techie reading.
- Peer Reviewed Research Studies on Wi-Fi Radiation
https://ehtrust.org/science/peer-reviewed-research-studies-on-wi-fi/ - National Institute of Health
https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/high-exposure-radio-frequency-radiation-associated-cancer-male-rats - Science Direct
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0013935118300355
Video
TED Talks – Engineer Jeromy Johnson on RF hazards and mitigation.
WiFi Best Practices
How should you properly deploy WiFi? The key to reducing unnecessary exposure is two fold; consider both distance and time. It is simply recommended that you place WiFi routers and antennae at least 1 to 2 meters from anyone who may be seated or sleeping for any extended period of time. Read more about wifi signal propagation patterns.
When designing a home or office WiFi system, place routers and antennae in seldom occupied areas, like lobbies, hallway intersections or in areas where people do not linger for long periods of time, like around printers or photocopy machines. Limiting long term exposure is key.
EMF Meter,Advanced GQ EMF-390 Multi-Field Electromagnetic Radiation 3-in-1 EMF ELF RF meter, 5G Cell Tower Smart meter Wifi Signal Detector RF up to 10GHz with Data Logger and 2.5Ghz Spectrum Analyzer
EMF Meter HF-B3G Triple Axis HF RF Analyzer and Detector Calibrated Measuring Emissions from Cell Phones, Smart Meters, Cell Towers, Microwave, Bluetooth - for EMF Home Inspections Free Support
Advanced GQ EMF-380 V2 Multi-Field Electromagnetic Radiation 3-in-1 EMF ELF Meter RF Spectrum Analyzer Ghost Cell Tower Smart Meter WiFi hiden Spy Camera Signal Bug Detector RF up to 8G
$100.00Improper WiFi Antennae Placement
The wrong place to place routers is near seating or sleeping quarters. For example, placing a WiFi router next to your bed or couch is probably not a good idea. Placing routers or antennae next to you office desk is also unwise. Place the router or antenna as far away from workers as possible.
As a simple analogy, think of the WiFi signal as a heat lamp. If you are close enough to feel the heat, you’re too close. As you back away, you feel much less heat due to the inverse square law of signal propagation. When you are 1 to 2 meters away from a heat lamp, you feel almost nothing. That’s a safe distance.
Although infrared heat energy is a much lower frequency, the propagation analogy holds, although 2.4 Ghz would be spaced apart by half a wavelength and look like more Swiss cheese.
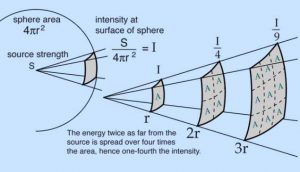
As you can clearly see by the graphic above, the signal continues to weaken as distance increases. The key is to stay far enough away to mitigate any issues and to always err on the side of caution.
To view Wifi signal propagation in 3D, check out this ingenious home brew project.
But wait, the FCC says it’s safe…
The FCC, FDA and the IT lobby will tell you that the minimum safe distance for Wifi routers is about 8 inches. Read that again. It says MINIMUM. This does not mean that the signal is completely harmless outside that range. In many cases users are being bombarded by multiple access points and devices. SAR (Specific Absorption Rate) ratings are published using outdated methods. This is why that since 2015 there has been a call for the FCC to re-evaluate outdated SAR guidelines and for companies to adopt safe Wifi usage policies to protect their workforce.
The following video explains EMF exposure in detail…
More…
Consumer Reports:
https://www.consumerreports.org/radiation/do-i-need-to-worry-about-radiation-from-wifi-and-bluetooth-devices/
The Bottom Line…Distance and Time.
When deploying Wifi in an office environment, consider the distance of antennas to workers who remain seated within a meter or two. At home, be aware of the location of Wifi IoT devices like Roku, Alexa or smart home hubs. In sleeping areas, try to maximize the distance of wifi devices.
For example; a cell phone set to hot spot mode should not be placed on your head board. If you must sleep with your phone, turn off wifi sharing or set it to airplane mode.
The bottom line is to place RF devices in places where people do not dwell for long periods of time. Simple precautions like this can eliminate your RF exposure.








![[ Versatile RF detector and High Frequency (HF) analyzer] Reliably measures emissions from cell phones, cell towers, smart meters, and modems, covering a wide range of high-frequency sources [ Beginner and Advanced User Friendly ] Simple enough for b...](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/31VO-bN7MVL._SL160_.jpg)